A Complete Guide to Video Analytics
This guide covers the origins of video analytics, the use of video intelligence in multiple industry sectors, stand-out analytics advances and future AI applications.

Are you looking for a video analytics solution for your business?
Contact us now to find out more about our Smart Analytics software.
What are video analytics?
Video analysis is the processing of video footage in real-time and the transformation of captured information into intelligent data. The analytics process automatically generates descriptions of video activity (or ‘metadata’) to detect and track objects such as people and vehicles.
Video analysis software is generally installed to generate objective data intended to inform decision making and ‘best next actions.’ Today, ‘next actions’ cover a vast range of possibilities, from security interventions to procedural updates and lifestyle management.
Video analytics software is fast and accurate – often supported by artificial intelligence – and have largely replaced manual video footage review, which was and is inefficient, costly, and prone to human error.
Video analysis is most frequently deployed to overcome human limitations when it comes to coping accurately with large volumes of data.
Video analytics solutions are also used for video data mining, which involves the analysis of historical data to discover insights such as trends and patterns.
The evolution of video analytics: surveillance roots stimulate video analytics debate
Since the widespread introduction of CCTV in the 1970s, surveillance of the public has been met with a mix of sceptical and positive reviews. Opinion is split between those who see video analytics as an intrusion on privacy and those who value its effectiveness for preventing and punishing criminal activity.
However, over the years since video analytics solutions were introduced, the use of what is known as smart video technology has spread to inform the analysis of every type of activity, in business, sports and people’s lifestyles, and has extended far beyond security operations.
How does video analytics work?
Depending on the particular use case, the architecture of a solution may vary.
Video content analysis can be conducted in real time, by configuring the system to trigger alerts for specific events and incidents that occur in the moment, or in post processing, by performing advanced searches to facilitate extensive analysis.
Feeding video data to the system
The data to be analysed can be ingested from various video sources. The most common are CCTV cameras, traffic cameras and online video feeds. The majority of video sources can be integrated into the analytics solution.
The breadth of the video coverage and the amount of data collected determine the breadth and, to some extent, the accuracy of the analytics.
Central processing vs edge processing
Video analysis software can be run centrally on servers located in a monitoring station, in other words central processing. Alternatively, analysis can be embedded in the cameras themselves, which is known as edge processing.
The selection of central and edge processing is often determined by bandwidth and storage considerations. Legacy systems catered only for central processing, which lends itself to extensive post processing, while edge processing can be pre-configured only to send data related to specific event types.
Defining situations and training models
After installation, it is possible to introduce models and train the system to become increasingly accurate at identifying events. For example, recognising vehicle types such as moving and stationary trucks, cars and motorbikes. In this instance, the data can be used to detect a possible crash.
Classifying objects such as people and vehicles, animals and man-made structures, in combination with local geographical data, enables the system to become smarter over time.
Image datasets are available that simplify the training of new models, while pre-trained models are available to fine-tune models for a specific use case.
Growing public understanding of the value of video analytics
Video analytic software is now capable of producing insights and reports that facilitate increased operational efficiency across all business types, by measuring and optimising what we do and how we act.
Perhaps video analytics entered the public’s consciousness most recently and most comprehensively through its development in sports.
Football fans cannot escape the controversy and ongoing human errors that surround the use of the otherwise accurate VAR (video assisted referee). Then again, technological change has always been viewed with scepticism, until it proves its value.
Used correctly, video analysis of athletic performance provides objective insights into anything observable, repeatable and improvable with a player’s movement and technique. Technology helps trainers to plan sports development and enables managers to make tactical decisions based on live data, such as distance covered, pitch heatmaps, passing accuracy, and more.
The application of video analytics in the wider community
Almost every industry around the world has reaped the rewards of wider video analysis. Those benefitting include operators making use of video intelligence in retail, commercial offices, warehouses and workspaces, as well as in the travel, transport, leisure, education and medical sectors.
Retailers benefit most from video analytics
Retail is the industry sector that has benefited most from the use of video analytics services. Smart video analysis used in smart zones and retail is so advanced that retailers have the ability to gain a deep understanding of consumer behaviour.
Bricks-and-mortar retailers can make the physical space within which they operate work better for them by capturing unprecedented levels of insight and business intelligence. Such data was historically very difficult to acquire. Today, retailers have at their fingertips actionable data on traffic flow, workforce management, store design and merchandising, supply, security and compliance.
Video intelligence helps retail businesses to align their targets for personnel, finances, overheads and margins, with new evidence-based data.
How retail video analytics may become commonplace in the future is indicated by emerging outlets such as Amazon Go. Video analytics eliminate check-outs to simplify the customer’s shopping experience and enable customers to walk out of the store having been charged automatically for the items they have selected.
The benefits of healthcare video analytics
Healthcare staff from surgeons to nurses benefit in many ways from the use of smart video analytics services. Surgeons use video analytics as a way of detecting minute mistakes, which improves clinical procedures over time in a way that was not previously possible.
The training of healthcare professionals is improved by the advent of remote procedure observation. Hospitals are generally able to improve the way they operate owing to regular insights into staff processes, and staff interaction, for example with people and equipment.
Video analytics in healthcare support incremental improvements that contribute to the health of patients and senior management’s awareness of best practice.
Away from hospitals, video analytics solutions are deployed to manage the health and safety of potentially vulnerable people, where cameras can detect in real time if a person has fallen, such as an elderly person living alone or a remote worker operating in a hazardous environment.
Video analysis in education supports continual innovation
The education sector relies on continual innovation and adaptation. Individuals must find new ways of learning about themselves and improve in a cycle of continuous professional development.
Teachers are asked to become more self-aware and improve the way they present their lessons in order to enhance the student experience and learning environment.
Video analytics services enable experts to provide constructive feedback to teachers at every stage of their development in order to help them become and remain effective educators.
Transport: video content analytics keep us on the move
American transportation entrepreneur, Robin Chase, co-founder of Zipcar, said:
“Transportation is the centre of the world! It is the glue of our daily lives. When it goes well, we don't see it. When it goes wrong, it negatively colours our day, makes us feel angry and impotent, and curtails our possibilities.”
Transport is a necessity for the vast majority of people. When transport operators have issues, they have a measurable impact and are widely publicised. As a result, it is natural that video analysis is integrated into the control and monitoring of most transport types.
Rail and air travel, motoring, and interactions at transport hubs have all been enhanced by the use of video analysis. For example, video analysis combined with improved artificial intelligence improves traffic flow management and reduces congestion. Video analysis is also used to detect suspicious behaviour and anticipate potential dangers before they develop.
Analytics at work: how Transport for London (TfL) makes widespread use of video analytics
TfL’s explanation of its use of video analytics is informative and encouraging for privacy sceptics. The bulk of TfL’s CCTV operations support TfL’s statutory functions, in particular, to deliver “integrated, efficient and economic transport facilities and services to, from and within Greater London.” The main purposes of TfL’s CCTV operations and video analytics include:
Protecting the health and safety of employees, customers and members of the public
Protecting property and other infrastructure
The management and investigation of major incidents
Preventing and detecting crime and antisocial behaviour
Realtime traffic monitoring
Supporting the efficient management and operation of our road and rail networks
Video analytics are also used to create a visual summary of the operational changes TfL makes from time to time. Examples include: improvements to the layout of road junctions, or cycle lanes, or where traffic signal timings ae amended. Videos are used to demonstrate how changes contribute to the Mayor's Transport Strategy and other initiatives such as the Healthy Streets Approach.
TfL emphasises that the focus of any photographs or videos is the road network itself and not individual pedestrians, vehicles or cyclists. When personal data is captured inadvertently, redaction (blurring) is used to minimise the extent that people and cars are recognisable.
Video analytics are key in in the development of smart cities when an increase in traffic can result in an increase in accidents and traffic jams if adequate traffic management measures are not taken.
Security video analytics are in a class of their own
As we suggested at the outset, video surveillance was the original home of video analytics. It is therefore not surprising that major advances in security applications have involved advanced analytics.
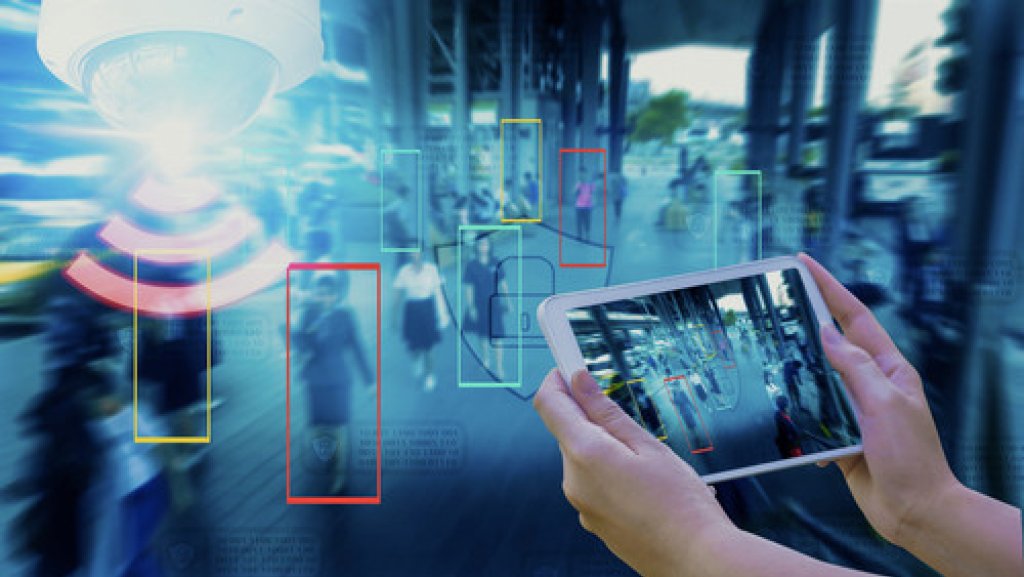
Facial recognition and license plate recognition are used to identify people and vehicles in real-time in order to make informed decisions. The reasons for using video intelligence may range from searching for a suspect to detecting missing cars and persons, in both ‘live’ and stored video footage.
Crowd management is another key function of security systems. Video analysis tools can help to manage busy shopping malls, hospitals, stadiums and transport hubs. Video intelligence is used to trigger alerts when an occupancy threshold is reached, or when prohibited movement is detected.
One of the latest developments in video analytics is camera analytics software, or ‘edge’ processing. ‘Edge’ processing eliminates the need for central servers as the video processing is embedded in the cameras themselves.
Facit: analytics, operations, compliance
If you are considering maximising intelligence available to you via CCTV data, we would be delighted to discuss video analytics software, operations management and compliance automation, and how we can help you lead the AI revolution.